Jackson Annotations for JSON
3 CommentsJackson is a suite of data-processing tools for Java comprising of three components:
- Streaming (jackson-core) defines low-level streaming API and includes JSON-specific implementations.
- Annotations (jackson-annotations) contains standard Jackson annotations.
- Databind (jackson-databind) implements data-binding (and object serialization) support on streaming package. This package depends both on streaming and annotations packages
In this post, I will explain the Java objects to JSON data-binding using Jackson annotations. I will take up each of the Jackson annotations and explain with code snippets how to use them. Each annotation usage is accompanied with proper test cases.
Jackson Serialization and Deserialization Annotations
The Jackson library provides annotations that you can use in POJO’s to control both serialization and deserialization between POJOs and JSON. Below are annotations used in both serialization and deserialization operations:
@JsonIgnore@JsonIgnoreProperties@JsonIgnoreType@JsonAutoDetect
@JsonIgnore
The @JsonIgnore annotation marks a field in a POJO to be ignored by Jackson during serialization and deserialization. Jackson ignores the field in both JSON serialization and deserialization. An example of Java class that uses the @JsonIgnore annotation is this.
IgnoreDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serializationanddeserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
public class IgnoreDemoBean {
@JsonIgnore
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "IgnoreDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test class to the @JsonIgnore annotation is this.
IgnoreDemoBeanTest.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serializationanddeserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.not;
import static org.hamcrest.core.IsEqual.equalTo;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class IgnoreDemoBeanTest {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper ;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception{
objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception{
objectMapper = null;
}
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonIgnore()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new IgnoreDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("productId")));
}
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonIgnore() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"personId\": 231, \"name\": \"Mary Parker\"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
IgnoreDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, IgnoreDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(not(equalTo(231L))));
}
}
The output on running the test in IntelliJ is this.
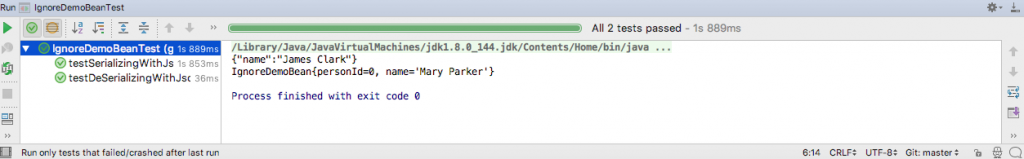
As you can see, the @JsonIgnore annotation ignored the field personId during serialization and deserialization.
@JsonIgnoreProperties
The @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation is used at the class level to ignore fields during serialization and deserialization. The properties that are declared in this annotation will not be mapped to the JSON content.
Let us consider an example of Java class that uses the @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation.
IgnorePropertiesDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serializationanddeserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@JsonIgnoreProperties({"userId", "gender"})
public class IgnorePropertiesDemoBean {
public long userId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
public String gender = null;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "IgnorePropertiesDemoBean{" +
"userId=" + userId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test code to the @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation is this.
IgnorePropertiesDemoBeanTest
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serializationanddeserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.not;
import static org.hamcrest.core.IsEqual.equalTo;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class IgnorePropertiesDemoBeanTest {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper ;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception{
objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception{
objectMapper = null;
}
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonIgnoreProperties()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new IgnorePropertiesDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("userId")));
}
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonIgnoreProperties() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"userId\": 231, \"name\": \"Mary Parker\", \"gender\": \"male\"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
IgnorePropertiesDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, IgnorePropertiesDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.userId, is(not(equalTo(231L))));
}
}
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
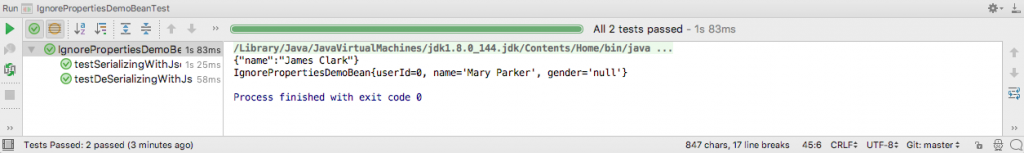
As you can see, the @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation ignored the field userId and gender both during serialization and deserialization.
@JsonIgnoreType
The @JsonIgnoreType annotation is used to mark a class to be ignored during serialization and deserialization. It marks all the properties of the class to be ignored while generating and reading JSON. An example of Java class that uses the @JsonIgnoreType annotation is this.
IgnoreTypeDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serializationanddeserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreType;
public class IgnoreTypeDemoBean {
@JsonIgnoreType
public static class Address {
public String doorNumber = null;
public String streetName = null;
public String pinCode = null;
public String city = null;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"doorNumber='" + doorNumber + '\'' +
", streetName='" + streetName + '\'' +
", pinCode='" + pinCode + '\'' +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
public Address address = new Address();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "IgnoreTypeDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
}
The test code to the @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation is this.
IgnoreTypeDemoBeanTest.java
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
@JsonAutoDetect
The @JsonAutoDetect annotation is used at the class level to tell Jackson to override the visibility of the properties of a class during serialization and deserialization. You can set the visibility with the following elements:
creatorVisibilityfieldVisibilitygetterVisibilitysetterVisibilityisGetterVisibility
The JsonAutoDetect class defines public static constants that are similar to Java class visibility levels. They are:
ANYDEFAULTNON_PRIVATENONEPROTECTED_AND_PRIVATEPUBLIC_ONLY
Let us consider an example of Java class that uses the @JsonAutoDetect annotation.
AutoDetectDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serializationanddeserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
@JsonAutoDetect(fieldVisibility = JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY)
public class AutoDetectDemoBean {
private long personId = 123L;
private String name = "James Clark";
public long getPersonId() {
return personId;
}
public void setPersonId(long personId) {
this.personId = personId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "IgnoreDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test code to the @JsonAutoDetect annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonAutoDetect()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new AutoDetectDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("123"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
}
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
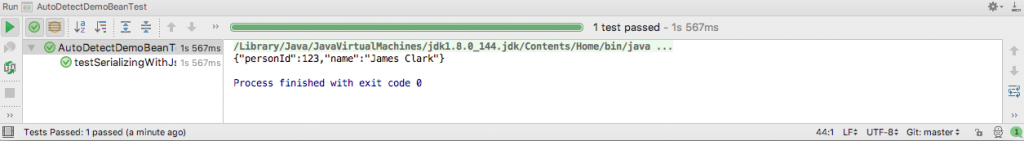
Jackson Serialization Annotations
Jackson provides several annotations that you can use in POJO’s to serialize Java objects to JSON. These annotations are:
@JsonValue@JsonInclude@JsonGetter@JsonAnyGetter@JsonPropertyOrder@JsonRawValue@JsonSerialize@JsonRootName
@JsonValue
The @JsonValue annotation is used at the method level. This annotation tells Jackson to use this method to generate the JSON string from the Java object.
Typically, if you want to print a serialized object, you override the toString() method. But, by using the @JsonValue annotation, you can define the way in which the Java object is to be serialized.
Note: Jackson omits any quotation marks inside the String that is returned by the custom serializer.
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonValue annotation.
ValueDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonValue;
public class ValueDemoBean {
@JsonProperty
private long personId = 123L;
@JsonProperty
private String name = "James Clark";
@JsonValue
public String toJson(){
return this.name+","+this.personId+","+this.toString();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ValueDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
In order to explain the difference between the serialized object with and without the @JsonValue annotation, the code includes the toString() method. You can also run the code without overriding the toString() method.
The code to test the @JsonValue annotation is this.
ValueDemoBeanTest
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.not;
import static org.hamcrest.core.IsEqual.equalTo;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class ValueDemoBeanTest {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception{
objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception{
objectMapper = null;
}
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonValue() throws JsonProcessingException{
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new ValueDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark,123"));
}
}
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
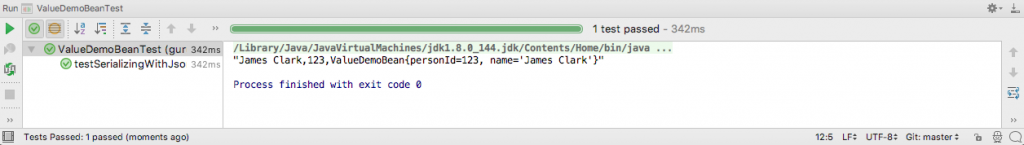
As shown in the preceding figure, the Java object is serialized by Jackson by calling the defined method toJson(). The quotation marks are added by Jackson.
@JsonInclude
The @JsonInclude annotation is used to exclude properties or fields of a class under certain conditions. This is defined using the JsonInclude.Include enum. This enum contains constants, that determine whether or not to exclude the property. The constants are:
ALWAYSNON_DEFAULTNON_EMPTYNON_NULL
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonInclude annotation.
IncludeDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)
public class IncludeDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String name = null;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "IncludeDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test code to the @JsonInclude annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonInclude() throws JsonProcessingException{
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new IncludeDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("123"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("name")));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
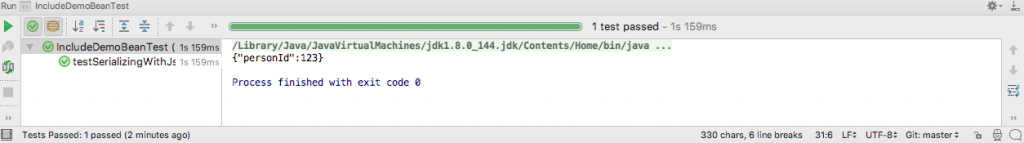
As shown in the preceding figure, the JSON string does not contain the property name as it is initialized to null.
@JsonGetter
The @JsonGetter annotation is used to customize the generated JSON keys. This is accomplished with the value argument of @JsonGetter. The value passed is the name that should be used as the JSON key.
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonGetter annotation.
GetterDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonGetter;
public class GetterDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String personName = "James Clark";
@JsonGetter(value = "person-id")
public long getPersonId() {
return personId;
}
@JsonGetter(value = "person-name")
public String getPersonName() {
return personName;
}
}
The code to test the @JsonGetter annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonGetter() throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new GetterDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("person-id"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("person-name"));
}
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.

As you can see in the example, the Java object is serialized with the property names that you defined using the @JsonGetter annotation. Without the annotations, the serialized JSON would contain the property names: personId and personName.
@JsonAnyGetter
The @JsonAnyGetter annotation can be used when you don’t want to declare a property or a method for every possible key in JSON. This annotation is used on the getter methods, which enables you to use a Map to hold all your properties that you want to serialize.
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonAnyGetter annotation.
AnyGetterDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAnyGetter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AnyGetterDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String personName = "James Clark";
private Map properties = new HashMap();
@JsonAnyGetter
public Map getProperties() {
return properties;
}
}
The code to test the @JsonAnyGetter annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonAnyGetter() throws JsonProcessingException {
AnyGetterDemoBean bean = new AnyGetterDemoBean();
Map<String, String > stringMap = bean.getProperties();
stringMap.put("emailId","[email protected]");
stringMap.put("gender","male");
String jsonString = objectMapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(bean);
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("emailId"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("gender"));
}
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
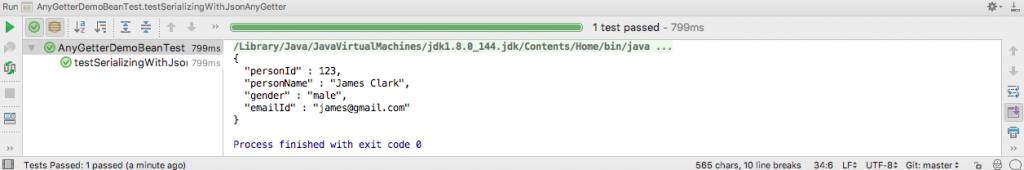
As you can see, all the properties are serialized as the properties of AnyGetterDemoBean object.
@JsonPropertyOrder
The @JsonPropertyOrder annotation tells Jackson to serialize the Java object to JSON, in the order specified as the arguments of the annotation. This annotation also allows partial ordering. The properties are first serialized in the order, in which they are found. Followed by any other properties not included in the annotation.
Let us consider an example of Java class that uses the @JsonPropertyOrder annotation.
PropertyOrderDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonPropertyOrder;
@JsonPropertyOrder({"name", "personId"})
public class PropertyOrderDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String name = "James Clark";
}
The test code to the @JsonPropertyOrder annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonPropertyOrder() throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new PropertyOrderDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("123"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
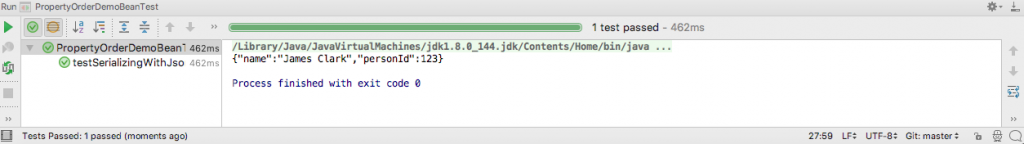
As you can see the result, the name property is first serialized before the personId. Without the @JsonPropertyOrder annotation, the object would have been serialized in the order found in the class.
@JsonRawValue
The @JsonRawValue annotation is used on methods and fields. It tells Jackson to serialize the field or property as declared. For example, if you have a String field in your Java class, the JSON value that Jackson generates is enclosed within quotes (” “). But when you annotate the field with @JsonRawValue, Jackson omits the quotes.
Let us consider an example Java class that explains the use of @JsonRawValue.
RawValueDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonRawValue;
public class RawValueDemoBean {
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonRawValue
public String address = "{\"doorNumber\": 1234, \"street\": \"phase-1\", " +
"\"city\": \"New York\"}";
}
Here, the address field is a JSON string. This JSON string will be serialized as a part of the final JSON string of the RawValueDemoBean object.
The test code to test the @JsonRawValue annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonRawValue() throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new RawValueDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("{\"doorNumber\": 1234, " +
"\"street\": \"phase-1\", \"city\": \"New York\"}"));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
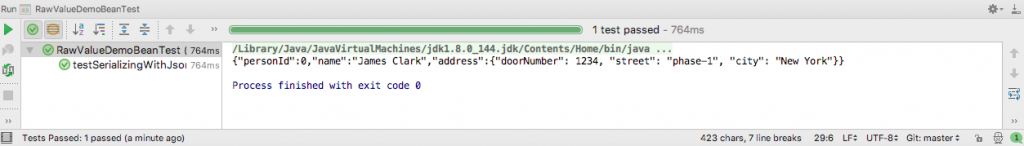
As you can see, the final JSON string of the Java object is generated as defined in the POJO class omitting the quotes.
@JsonSerialize
The @JsonSerialize annotation is used tell Jackson to use the declared custom serializer during the serialization of the field, which is marked with this annotation. Let us consider a POJO that uses the @JsonSerialize annotation.
SerializeDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize;
import guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.custom.CustomDateSerializer;
import java.util.Date;
public class SerializeDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonSerialize(using = CustomDateSerializer.class)
public Date activeDate;
public void setActiveDate(Date activeDate) {
this.activeDate = activeDate;
}
}
Next, let us define a custom serializer that will serialize the activeDate field with a specific format.
CustomDateSerializer.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.custom; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerationException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializerProvider; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.StdSerializer; import java.io.IOException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class CustomDateSerializer extends StdSerializer{ private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss"); public CustomDateSerializer(){ this(null); } public CustomDateSerializer(Class t) { super(t); } @Override public void serialize(Date date, JsonGenerator jsonGenerator, SerializerProvider serializerProvider) throws IOException { jsonGenerator.writeString(simpleDateFormat.format(date)); } }
The code to test the @JsonSerialize annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonSerialize() throws JsonProcessingException,ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss");
String date = "29-09-2017 10:00:00";
Date newDate = simpleDateFormat.parse(date);
SerializeDemoBean bean = new SerializeDemoBean();
bean.setActiveDate(newDate);
String jsonString = objectMapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(bean);
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("123"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("29-09-2017 10:00:00"));
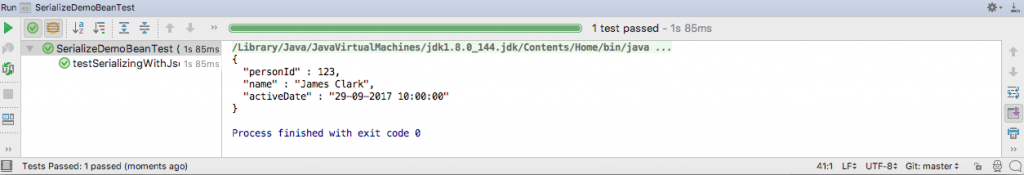
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
@JsonRootName
The @JsonRootName annotation can be used to tell Jackson to wrap the object to be serialized with a top-level element. You can pass the name as a parameter to the @JsonRootName annotation. Let us consider that you want to wrap your serialized Java object with the key user.
Here is an example of Java class that uses the @JsonRootName annotation.
RootNameDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.serialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonRootName;
@JsonRootName(value = "user")
public class RootNameDemoBean {
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
}
The code to test the @JsonRootName annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonRootName() throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.enable(SerializationFeature.WRAP_ROOT_VALUE)
.writeValueAsString(new RootNameDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("user"));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
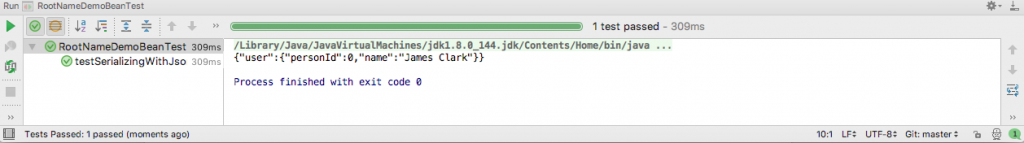
As you can see, the fields personId and name are wrapped within the user, where the latter is the key, and the former is the value of the property of the generated JSON.
Deserialization Annotations
Let us explore the JSON annotations that can be used to control deserialization of JSON into POJOs. The Jackson deserialization annotations are:
@JsonSetter@JsonAnySetter@JsonCreator@JacksonInject@JsonDeserialize
@JsonSetter
The @JsonSetter annotation tells Jackson to deserialize the JSON into Java object using the name given in the setter method. Use this annotation when your JSON property names are different to the fields of the Java object class, and you want to map them.
A Java class that uses the @JsonSetter annotation is this.
SetterDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.deserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonSetter;
public class SetterDemoBean {
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonSetter("id")
public void setPersonId(long personId) {
this.personId = personId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SetterDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The @JsonSetter annotation takes the name of the JSON key that must be mapped to the setter method.
The test code to test the @JsonSetter annotation is this.
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonSetter() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"id\": 231, \"name\": \"Mary Parker\"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
SetterDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, SetterDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(equalTo(231L)));
}
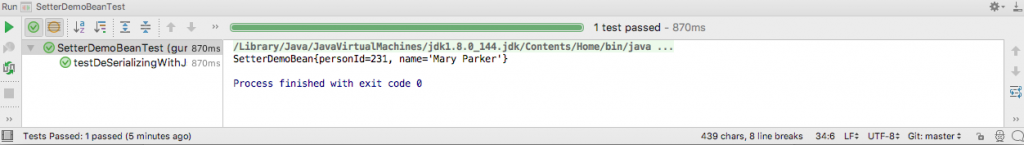
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
As you can see, the JSON to be serialized has a property id. But no field in the POJO matches this property. Now how will Jackson read this JSON? Here is where the @JsonSetter annotation can be used to map the property id to the field personId. This annotation instructs Jackson to use a setter method for a given JSON property.
@JsonAnySetter
The @JsonAnySetter annotation is used on setter methods of a Map field. Sometimes, you may find some JSON values that cannot be mapped to the fields in the Java object class. In such a case, the @JsonAnySetter captures the data and stores them in a Map.
A Java class that uses the @JsonAnySetter annotation is this.
AnySetterDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.deserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAnySetter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AnySetterDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String personName = "James Clark";
private Map properties = new HashMap();
@JsonAnySetter
public void setProperties(String key, String value){
properties.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AnySetterDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", personName='" + personName + '\'' +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
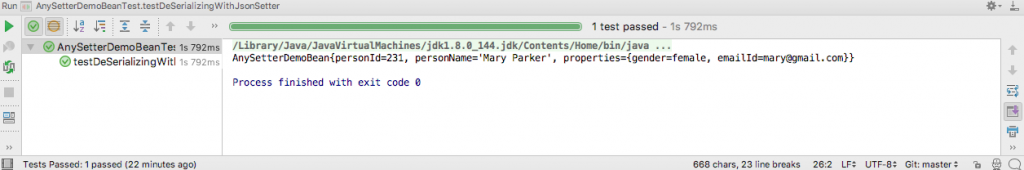
The test code to test the @JsonAnySetter annotation is this.
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonSetter() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"personId\": 231, \"personName\": \"Mary Parker\", \"emailId\": \"[email protected]\", \"gender\": \"female\"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
AnySetterDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, AnySetterDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.personName, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(equalTo(231L)));
assertEquals("female", bean.getProperties().get("gender"));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
@JsonCreator
The @JsonCreator annotation tells Jackson that the JSON properties can be mapped to the fields of a constructor of the POJO. This is helpful when the JSON properties do not match with the names of the Java object field names. The @JsonCreator annotation can be used where @JsonSetter cannot be used. For example, immutable objects which need their initial values to be injected through constructors.
An example of Java class that uses the @JsonCreator annotation is this.
CreatorDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.deserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonCreator;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class CreatorDemoBean {
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonCreator
public CreatorDemoBean(@JsonProperty("id") long personId, @JsonProperty("name") String name) {
this.personId = personId;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CreatorDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test code to test the @JsonCreator annotation is this.
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonCreator() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"id\": 231, \"name\": \"Mary Parker\"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
CreatorDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, CreatorDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(equalTo(231L)));
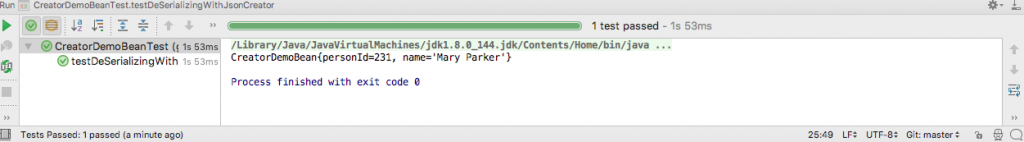
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
@JacksonInject
The @JacksonInject annotation is used to tell Jackson that particular values of the deserialized object will be injected and not read from the JSON string.
An example of Java class where the personId field is injected by Jackson is this.
JacksonInjectDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.deserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JacksonInject;
public class JacksonInjectDemoBean {
@JacksonInject
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "JacksonInjectDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
In order to inject values into a field, you can use the InjectableValues class. You need to configure ObjectMapper to read both, the injected values from injectableValues and the remaining values from the JSON string.
The test code to test the @JacksonInject annotation is this.
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJacksonInject() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"name\": \"Mary Parker\"}";
InjectableValues injectableValues = new InjectableValues.Std()
.addValue(long.class, 231L);
JacksonInjectDemoBean bean = new ObjectMapper().reader(injectableValues)
.forType(JacksonInjectDemoBean.class).readValue(jsonString);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(equalTo(231L)));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
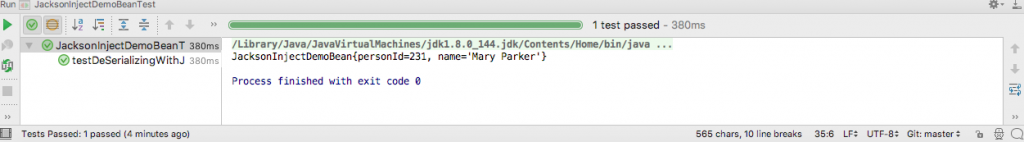
As you can see, the value for the field personId has been injected by Jackson and the other values are taken from the input JSON string.
@JsonDeserialize
The @JsonDeserialize annotation tells Jackson to use a custom deserializer while deserializing the JSON to Java object. To do so, you need to annotate the field to which you need to apply the custom deserializer.
A Java class that uses the @JsonDeserialize annotation is this.
DeserializeDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.deserialization;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonDeserialize;
import guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.custom.CustomDateDeserializer;
import java.util.Date;
public class DeserializeDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonDeserialize(using = CustomDateDeserializer.class)
public Date activeDate;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DeserializeDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", activeDate=" + activeDate +
'}';
}
}
The custom deserializer that is referenced by the preceding DeserializeDemoBean bean class is this.
CustomDateDeserializer.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.custom; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParser; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationContext; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.StdDeserializer; import java.text.ParseException; import java.io.IOException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class CustomDateDeserializer extends StdDeserializer{ private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss"); public CustomDateDeserializer(){ this(null); } public CustomDateDeserializer(Class c){ super(c); } @Override public Date deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException { String date = jsonParser.getText(); try { return simpleDateFormat.parse(date); } catch (ParseException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
Here, the CustomDateDeserializer class extends the StdDeserializer class with a generic type Date. The overriden deserialize() method returns the Date object.
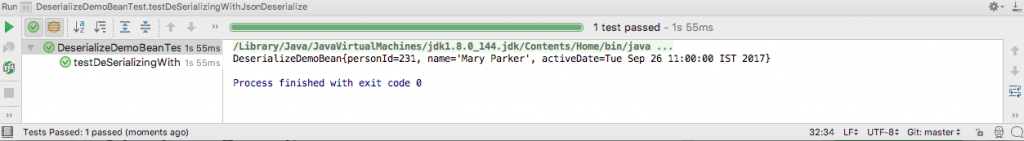
The test code to test the @JsonDeserialize annotation is this.
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonDeserialize() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"personId\": 231, \"name\": \"Mary Parker\", " +
"\"activeDate\":\"26-09-2017 11:00:00\"}";
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat =
new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss");
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
DeserializeDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, DeserializeDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(equalTo(231L)));
assertEquals("26-09-2017 11:00:00", simpleDateFormat.format(bean.activeDate));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
General Annotations
The general annotations are:
@JsonProperty@JsonFormat@JsonUnwrapped@JsonView@JsonManagedReferenceand@JsonBackReference@JsonIdentityInfo@JsonFilter
@JsonProperty
The @JsonProperty annotation is used to map property names with JSON keys during serialization and deserialization. By default, if you try to serialize a POJO, the generated JSON will have keys mapped to the fields of the POJO. If you want to override this behavior, you can use the @JsonProperty annotation on the fields. It takes a String attribute that specifies the name that should be mapped to the field during serialization.
You can also use @JsonProperty annotation during deserialization when the property names of the JSON and the field names of the Java object do not match.
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonProperty annotation.
PropertyDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class PropertyDemoBean {
@JsonProperty("person-id")
public long personId = 123L;
@JsonProperty("name")
public String name = "James Clark";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PropertyDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test code to test the @JsonProperty annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonProperty()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new PropertyDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
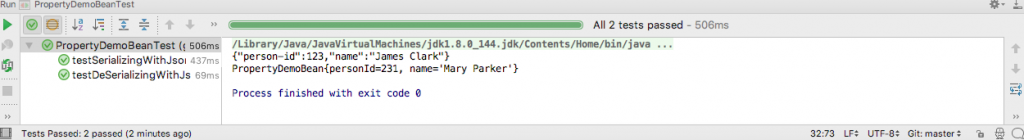
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("123"));
}
@Test
public void testDeSerializingWithJsonProperty() throws IOException {
String jsonString = "{\"person-id\": 231, \"name\": \"Mary Parker\"}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
PropertyDemoBean bean = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, PropertyDemoBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
assertThat(bean.name, is(equalTo("Mary Parker")));
assertThat(bean.personId, is(equalTo(231L)));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
@JsonFormat
The @JsonFormat annotation is used to tell Jackson that the format in which the value for a field is serialized. It specifies the format using the JsonFormat.Shape enum.
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonFormat annotation to modify the Date and Time format of an activeDate field.
FormatDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import java.util.Date;
public class FormatDemoBean {
@JsonProperty("person-id")
public long personId = 123L;
@JsonProperty("name")
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern = "dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss")
@JsonProperty("active-date")
public Date activeDate;
public FormatDemoBean() {
}
public void setActiveDate(Date activeDate) {
this.activeDate = activeDate;
}
}
The test code to test the @JsonFormat annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonFormat()
throws JsonProcessingException, ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss");
simpleDateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
String dateAndTime = "26-09-2017 11:00:00";
Date date = simpleDateFormat.parse(dateAndTime);
FormatDemoBean fb = new FormatDemoBean();
fb.setActiveDate(date);
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(fb);
System.out.println(jsonString);
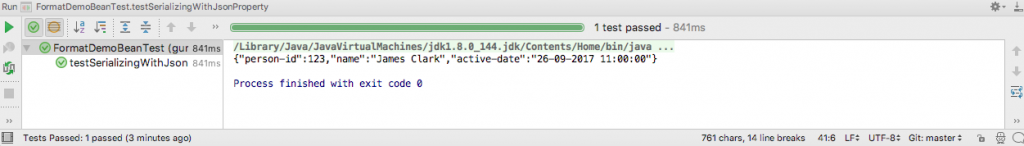
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("123"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("26-09-2017 11:00:00"));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
@JsonUnwrapped
The @JsonUnwrapped annotation unwraps the values during serialization and deserialization. It helps in rendering the values of a composed class as if they belonged to the parent class. Let us consider an example of Java class that uses the @JsonUnwrapped annotation.
UnwrappedDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonUnwrapped;
public class UnwrappedDemoBean {
public static class Address {
public String doorNumber = "12";
public String streetName = "phase-1";
public String pinCode = "123456";
public String city = "New York";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"doorNumber='" + doorNumber + '\'' +
", streetName='" + streetName + '\'' +
", pinCode='" + pinCode + '\'' +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonUnwrapped
public Address address = new Address();
}
In this example, the Address class is inside the UnwrappedDemoBean class. Without the @JsonUnwrapped annotation, the serialized Java object would be similar to this.
{"personId":0,
"name":"James Clark", "address":{"doorNumber":"12","streetName":"phase-1","pinCode":"123456","city":"New York"}
}
Let us see what happens when you use the @JsonUnwrapped annotation.
The test code to test the @JsonUnwrapped annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonUnwrapped()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new UnwrappedDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("address")));
}
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
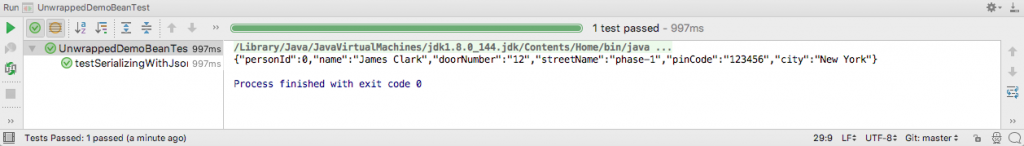
As you can see, the Address object is unwrapped and is displayed as the properties of the parent class UnwrappedDemoBean.
@JsonView
The @JsonView annotation is used to include or exclude a property dynamically during serialization and deserialization, and tells the view in which the properties are rendered. Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonView annotation with Public and Internal views.
ViewDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonView;
public class ViewDemoBean {
@JsonView(Views.Public.class)
@JsonProperty
public long personId = 0;
@JsonView(Views.Public.class)
@JsonProperty
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonView(Views.Internal.class)
@JsonProperty
public String gender = "male";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ViewDemoBean{" +
"personId=" + personId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The test code to test the @JsonView annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonView()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writerWithView(Views.Public.class)
.writeValueAsString(new ViewDemoBean());
String jsonStringInternal = objectMapper.writerWithView(Views.Internal.class)
.writeValueAsString(new ViewDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
System.out.println(jsonStringInternal);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("gender")));
assertThat(jsonStringInternal, containsString("gender"));
}As you can see in the test code, you need to configure the ObjectMapper to include which type of view must be used for writing the JSON from the Java object using the writerWithView() method.
The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
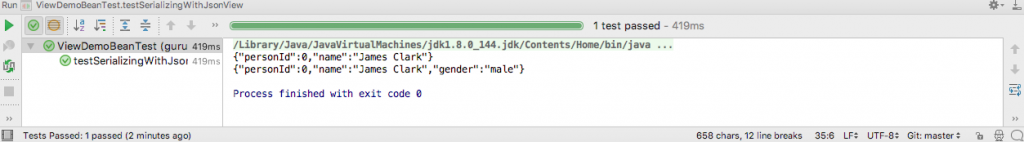
When the JSON is generated in the public view, only personId and name fields are serialized omitting the gender field. However, when JSON is generated in the internal view, all the fields are serialized.
@JsonManagedReference and @JsonBackReference
The @JsonManagedReference and @JsonBackReference annotation are used to create JSON structures that have a bidirectional relationship. Without this annotation, you get an error like this.
"com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonMappingException:Infinite recursion (StackOverflowError)"
Let us consider an example Java class that uses the @JsonManagedReference and @JsonBackReference annotations.
ManagedReferenceDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonManagedReference;
public class ManagedReferenceDemoBean {
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
@JsonManagedReference
public BackReferenceDemoBean manager;
public ManagedReferenceDemoBean(long personId, String name, BackReferenceDemoBean manager) {
this.personId = personId;
this.name = name;
this.manager = manager;
}
}
BackReferenceDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonBackReference;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BackReferenceDemoBean {
public long personId = 123;
public String name = "John Thomas";
@JsonBackReference
public List employees;
public BackReferenceDemoBean(long personId, String name) {
this.personId = personId;
this.name = name;
employees = new ArrayList();
}
public void addEmployees(ManagedReferenceDemoBean managedReferenceDemoBean){
employees.add(managedReferenceDemoBean);
}
}
The test code to test both @JsonManagedReference and @JsonBackReference annotations is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonManagedAndBackReference()
throws JsonProcessingException {
BackReferenceDemoBean demoBean = new BackReferenceDemoBean(123L, "Mary Parker");
ManagedReferenceDemoBean bean = new ManagedReferenceDemoBean(231L, "John Thomas", demoBean);
demoBean.addEmployees(bean);
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(bean);
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("John Thomas"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("231"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("employees")));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
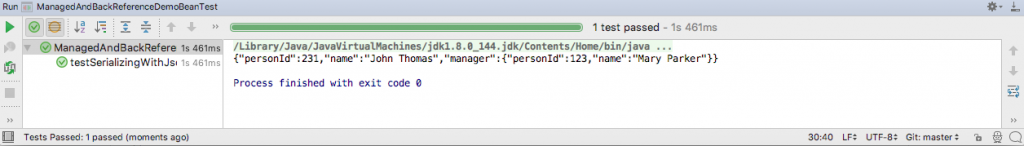
As you can see, the field marked with @JsonManagedReference is the forward reference which will be included during serialization. The field marked with @JsonBackReference is the back reference and is usually omitted during serialization.
@JsonIdentityInfo
The @JsonIdentityInfo tells Jackson to perform serialization or deserialization using the identity of the object. This annotation works similar to the @JsonManagedReference and @JsonBackReference annotations with the difference that @JsonIdentityInfo includes the back reference object.
Let us consider an example where the IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean has a bidirectional relationship with IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean using the @JsonIdentityInfo annotation.
IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIdentityInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.ObjectIdGenerators;
@JsonIdentityInfo(generator = ObjectIdGenerators.PropertyGenerator.class, property = "personId")
public class IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean {
public long personId = 0;
public String name = "James Clark";
public IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean manager;
public IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean(long personId, String name, IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean manager) {
this.personId = personId;
this.name = name;
this.manager = manager;
}
}
IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIdentityInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.ObjectIdGenerators;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@JsonIdentityInfo(generator = ObjectIdGenerators.PropertyGenerator.class, property = "personId")
public class IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean {
public long personId = 123;
public String name = "John Thomas";
public List employees;
public IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean(long personId, String name) {
this.personId = personId;
this.name = name;
employees = new ArrayList();
}
public void addEmployees(IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean identityInfoEmployeeDemoBean){
employees.add(identityInfoEmployeeDemoBean);
}
}
The test code to test the @JsonIdentityInfo annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonIdentityInfo()
throws JsonProcessingException {
IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean demoBean = new IdentityInfoManagerDemoBean(123L, "Mary Parker");
IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean bean = new IdentityInfoEmployeeDemoBean(231L, "John Thomas", demoBean);
demoBean.addEmployees(bean);
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(bean);
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("John Thomas"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("231"));
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("employees"));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
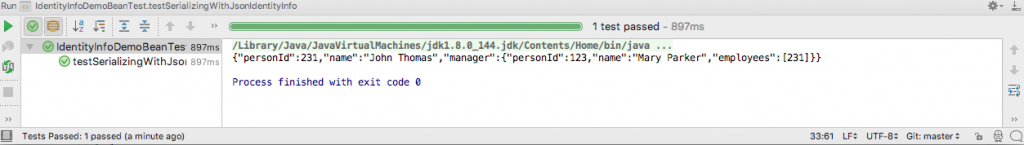
As you can see, the output gives the information about the employee with his manager details and information about the employees under the manager.
@JsonFilter
The @JsonFilter annotation is used to tell Jackson to use a custom defined filter to serialize the Java object. To define your filter, you need to use the FilterProvider class. This provider gets the actual filter instance to use. The filter is then configured by assigning the FilterProvider to ObjectMapper.
Let us consider an example of Java class that uses the @JsonFilter annotation.
FilterDemoBean.java
//package guru.springframework.blog.jsonannotation.domain.general;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFilter;
@JsonFilter("customFilter")
public class FilterDemoBean {
public long personId = 123L;
public String name = "James Clark";
public String gender = "male";
}
The test code to test the @JsonFilter annotation is this.
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonFilter()
throws JsonProcessingException {
FilterProvider filterProvider = new SimpleFilterProvider().
addFilter("customFilter",
SimpleBeanPropertyFilter.filterOutAllExcept("name"));
String jsonString = objectMapper.writer(filterProvider).
writeValueAsString(new FilterDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString("James Clark"));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString("123")));
}The output of running the test in IntelliJ is this.
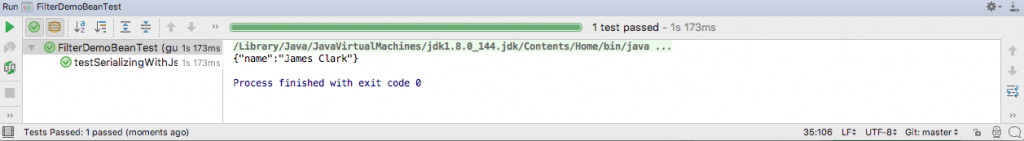
As you can see, the custom filter declared as the arguments of the @JsonFilter annotation extract only the name and filters out the other properties of the bean during serialization.
You can download the source code of this post from here.
























simonmichel
Your code in sample “AutoDetectDemoBean.java” is missing.
Best
shivani
nice writeup, from where we can download source code for the examples in your blog..
Nelson Visbal
In the first example “productId” doesn’t exists in the “IgnoreDemoBean.java” class
@Test
public void testSerializingWithJsonIgnore()
throws JsonProcessingException {
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new IgnoreDemoBean());
System.out.println(jsonString);
assertThat(jsonString, containsString(“James Clark”));
assertThat(jsonString, not(containsString(“productId”)));
}