EnumSet in Java
0 CommentsLast Updated on September 10, 2021 by jt
In Java, you use the enumeration type to represent a list of predefined constants. But, what if you want to implement a Set interface with the enumeration type, you have got EnumSet in Java to do so.
Enum constants are unique and have predefined length, as you can not define a new enum constant at runtime, therefore it allows Java API designers to highly optimize EnumSet. It is henceforth clearly stated that an EnumSet is a specialized Set collection to work with enum classes.
If you are not familiar to using enums in Java, you can check my post on Using Java Enums.
In this post, you will learn about using EnumSet in Java, its various methods and their implementation.
Important features of EnumSet
EnumSetcan contain onlyenumvalues and all the values should belong to the sameenum.- It does not allow adding null objects and throws
NullPointerExceptionif we try to do so. - It extends
AbstractSetclass and implementsSetInterface in Java. - The elements in
EnumSetare stored following the order in which they are declared in theenum. - It uses a fail-safe iterator that works on a copy, so it won’t throw a
ConcurrentModificationExceptionif the collection is modified when iterating over it. - It is not thread-safe, so we need to synchronize it externally if required.
Declaring an EnumSet
The declaration for java.util.EnumSet class is this.
public abstract class EnumSet<E extends Enum<E>>
Here, E specifies the elements. E must extend Enum, which enforces the requirement that the elements must be of the specified enum type.
Creating an EnumSet
In order to create an enum set, we must import the java.util.EnumSet package first.
Unlike other set implementations, the enum set does not have public constructors. We must use the predefined methods to create an enum set. The various methods of creating an EnumSet are as follows:
EnumSet using allOf(Size)
The allof() method creates an enum set that contains all the values of the specified enum type Size.
Here is the code for allof() method of creating EnumSet.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
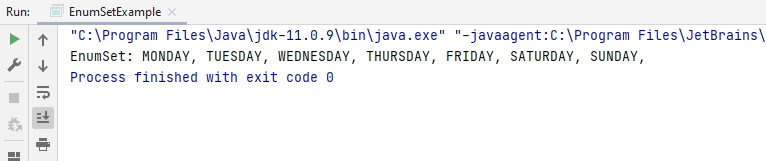
EnumSet days = EnumSet.allOf(Days.class);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + days);
}
}
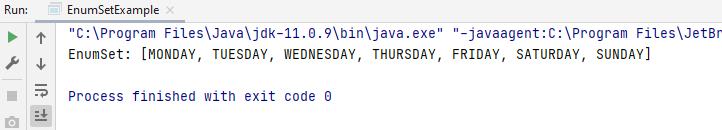
The preceding code defines an enum type, Days. The names of the enum type’s fields are in uppercase letters as they are constants. The allOf() method is used here to create an enum set that will be used to contain all of the elements in the specified elementType.
The output on running the code is this.
EnumSet using noneOf(Size)
The noneOf() method creates an empty enum set.
The code for noneOf() method is this.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumSet emptyDays = EnumSet.noneOf(Days.class);
System.out.println("Empty EnumSet: " + emptyDays);
}
}
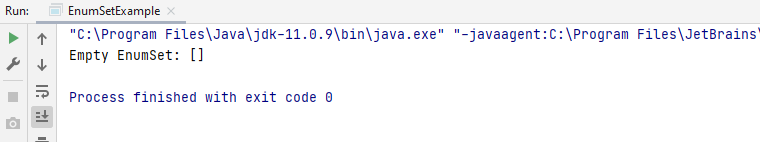
Here, the noneOf() method creates a null set of the type elementType.
This is the output of the preceding code.
EnumSet using range(e1, e2) Method
The range() method creates an enum set containing all the values of an enum between e1 and e2 including both values.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumSet rangeDays = EnumSet.range(Days.TUESDAY, Days.FRIDAY);
System.out.println("EnumSet: " + rangeDays);
}
}
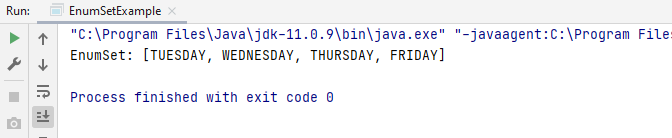
Thus, here Days from TUESDAY to FRIDAY will be added into the enum set.
The output on running the code in IntelliJ is this.
EnumSet using of() Method
The of() method creates an enum set containing the specified elements.
The code for of() method is this.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumSet days1 = EnumSet.of(Days.SUNDAY);
System.out.println("EnumSet1: " + days1);
EnumSet days2 = EnumSet.of(Days.SATURDAY, Days.SUNDAY);
System.out.println("EnumSet2: " + days2);
}
}
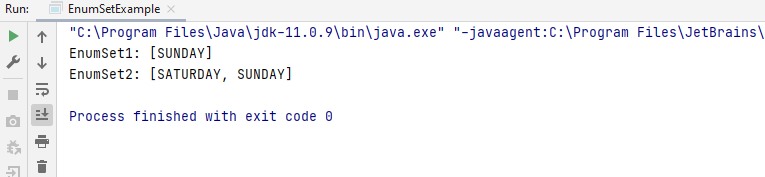
Thus, here only the specied days SUNDAY in days1 and SATURDAY and SUNDAY in days2 will be added in the enum set.
Here is the Output.
EnumSet Methods
The EnumSet class provides methods that allow us to perform various elements on the enum set.
Inserting elements to EnumSet
There are two ways to insert elements in anEnumSet
First is the add() method which inserts specified enum values to the enum set.
Secondly, the addAll() method inserts all the elements of the specified collection to the set.
Here is the code for both add() and addAll() methods.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumSet days1 = EnumSet.of(Days.SUNDAY);
System.out.println("EnumSet1: " + days1);
EnumSet days2 = EnumSet.of(Days.SATURDAY, Days.SUNDAY);
System.out.println("EnumSet2: " + days2);
// Using add method
days1.add(Days.MONDAY);
System.out.println("EnumSet Using add(): " + days1);
// Using addAll() method
days2.addAll(days1);
System.out.println("EnumSet Using addAll(): " + days2);
}
}
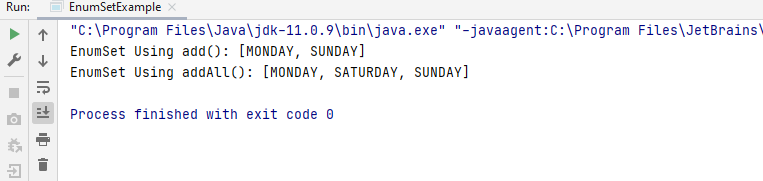
Thus, to the first EnumSet MONDAY gets added and in the next EnumSet using addAll() method all days get added.
This is the output for the preceding code.
EnumSet Iteration
To access elements of an enum set, we can use the iterator() method. In order to use this method, we must import the java.util.Iterator package.
The code for accessing the enum set elements is this.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumSet days = EnumSet.allOf(Days.class);
Iterator iterate = days.iterator();
System.out.print("EnumSet: ");
while (iterate.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterate.next());
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}
The output on running the code in IntelliJ is this.
Removing elements of EnumSet
There are two methods to remove elements from an enum set.
The remove()method removes the specified element from the enum set.
The removeAll() which removes all the elements from the enum set.
This is the code for removing elements from an enum set.
EnumSetExample.java
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumSetExample {
enum Days {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumSet days = EnumSet.allOf(Days.class);
// Using remove()
boolean value1 = days.remove(Days.FRIDAY);
System.out.println("Is FRIDAY removed? " + value1);
// Using removeAll()
boolean value2 = days.removeAll(days);
System.out.println("Are all elements removed? " + value2);
System.out.println(days);
}
}
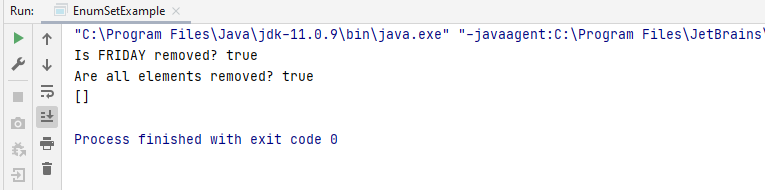
Here, the remove() method removes FRIDAY and then later on the removeAll() method removes all days from the enum set, therefore the value2 will be set to true.
The output on running the code in IntelliJ is this.
Summary
The EnumSet provides an efficient way to store enum values than other set implementations (like HashSet, TreeSet). An enum set only stores enum values of a specific enum. Hence, the JVM already knows all the possible values of the set. This is the reason why enum sets are internally implemented as a sequence of bits. Bits specifies whether elements are present in the enum set or not. The bit of a corresponding element is turned on if that element is present in the set.