Using ImmutableList in Java
0 CommentsThere are read-only wrappers over collections which are known as unmodifiable lists. These lists do not support any modification operations such as add, remove, and clear. Hence, these kinds of lists which guarantee that no change in the Collection object will ever be visible are termed as immutablelist.
The Java Collections framework provides the unmodifiableList() method. It is not safe to use it as the returned list is only truly immutable if nobody holds a reference to the original collection. Therefore, Guava, a Java-based library developed by Google provides a simple, easy-to-use immutable version of each standard Collection type. It includes its own Collection variations. It also provides an instance of ImmutableList that contains its own private data and will never change.
In this post, you will learn how to create and use ImmutableLists in Java.
Features of ImmutableLists
ImmutableListsare read-only as the elements of the list are fixed or constant after declaration.- An
UnsupportedOperationExceptiongets thrown if you try to add, delete or update elements in the List. - An
ImmutableListdoes not allow null element. If any attempt is made to create anImmutableListwith null element,NullPointerExceptionis thrown.
Class hierarchy
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection
↳ com.google.common.collect.ImmutableCollection
↳ com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList
The AbstractCollection class provides a skeletal implementation of the Collection interface. It is extended by ImmutableCollection, which is further extended by ImmutableList.
Creating an ImmutableList
Immutable Lists can be created by the following methods.
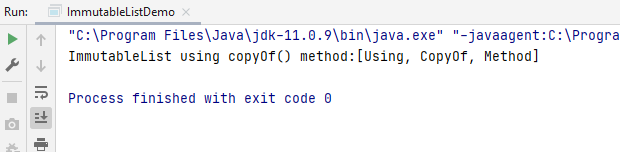
ImmutableList using ImmutableList.of() method
The ImmutableList.of() method returns an immutable list containing the given elements in order.
This is the code for the ImmutableList.of() method.
ImmutableListDemo.java
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
class ImmutableListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableList immutableList =
ImmutableList.of("Immutable", "Lists", "Java");
System.out.println(immutableList);
}
}
The output on running the code in IntelliJ is this.
ImmutableList using ImmutableList.copyOf() method
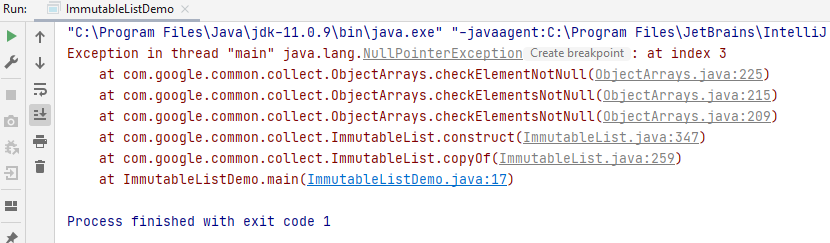
ImmutableList.copyOf() method returns an immutable list containing the elements of the specified list. It returns a NullPointerException if any of the elements is null.
The code for ImmutableList.copyOf() method is this.
ImmutableListDemo.java
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import java.util.*;
class ImmutableListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("Using", "CopyOf", "Method"));
ImmutableList immutableList1 = ImmutableList.copyOf(list);
List list1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("Using", "CopyOf", "Method", null));
ImmutableList immutableList2 = ImmutableList.copyOf(list1);
System.out.println("ImmutableList using copyOf() method" + ":" + immutableList1);
System.out.println("ImmutableList to insert null element" + ":" + immutableList2);
}
}
In line 9, you are using the copyOf() method to create immutableList1. In line 10, you are trying to add null element to the same list, which results in NullPointerException.
This is the output on running the code in IntelliJ.
And this is the output of when you try to add a null element to an immutable list.
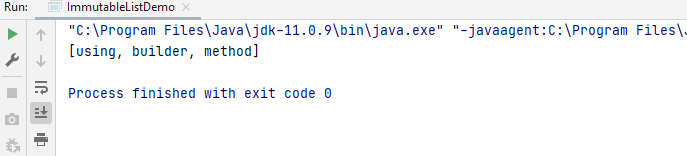
ImmutableList using Builder() method
The Builder() function helps to create a new ImmutableList or creates from an existing List.
Here is the code.
ImmutableListDemo.java
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
class ImmutableListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableList iList = ImmutableList.builder()
.add("using", "builder", "method")
.build();
System.out.println(iList);
}
}
Here is the output for the preceding code.
ImmutableList using Java 9 – Collection factory methods
The collection factory methods are only available for List, Set, and Map interfaces. The returned collection is structurally immutable, i.e., we cannot add elements, removed or replaced them from the collection.
This is the code for creating an immutable list using collection factory methods.
ImmutableListDemo.java
import java.util.*;
class ImmutableListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List immutableList2 = List.of("Using", "Java9", "factory", "method");
System.out.println(immutableList2);
immutableList2.add("ExceptionDemo");
System.out.println(immutableList2);
}
}
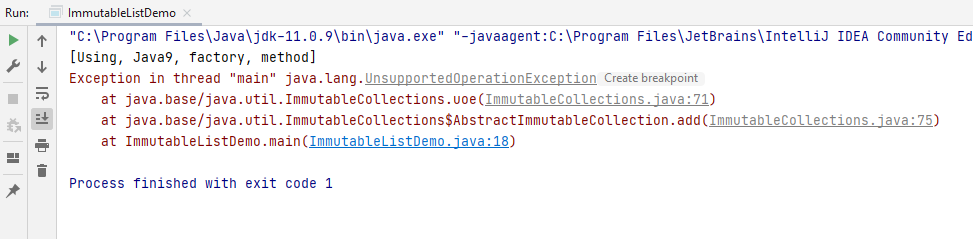
The output on running the code in IntelliJ is this.
Any modification operation will throw an UnsupportedOperationException as we tried to add ExceptionDemo to the already created ImmutableList.
Summary
It is clearly evident that you can create an unmodifiable List out of an existing ArrayList using either the core JDK, Google Guava, or Apache Commons Collections. Also Collections.unmodifiableList creates a wrapper around the same existing List such that the wrapper cannot be used to modify it. However we can still change original List.