Java String to Int
0 CommentsLast Updated on June 16, 2019 by Simanta
A common requirement while programming in Java is to convert String to int. UI inputs in Web-based HTML, JSP, or Thymeleaf templates are transferred to backend Java applications as strings. It is the application developer’s responsibility to perform any String to int conversions to fulfill business logic, such as calculating discounts, storing age, and so on.
In this post, I’ll discuss how to convert String in Java to int.
The Integer.parseInt Method
The Integer.parseInt() method takes as input a String and returns an int value.
The code to use this method is.
public int convertWithParseInt(String str){
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
return num;
}
Here is the test code in JUnit.
package springframework.guru;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
public class StringToIntConverterTest {
private StringToIntConverter stringToIntConverter;
String str;
@Before
public void setUp(){
str = "369";
stringToIntConverter=new StringToIntConverter();
}
@After
public void tearDown(){
str = null;
}
@Test
public void convertWithParseInt() {
int val= stringToIntConverter.convertWithParseInt(str);
System.out.println(val);
assertEquals(val, 369);
}
}
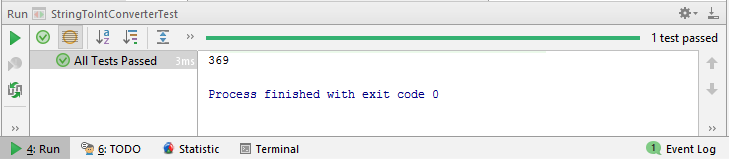
The output on running the test in InteliJ is this.
The Integer class also provides an overloaded parseInt() method that additionally accepts the radix (base) to be used while parsing.
Here is the code to use the overloaded method..
public int convertWithParseIntWithRadix(String str, int radix){
int num = Integer.parseInt(str, radix);
return num;
}
Here is the test code.
@Test
public void convertWithParseIntWithRadix() {
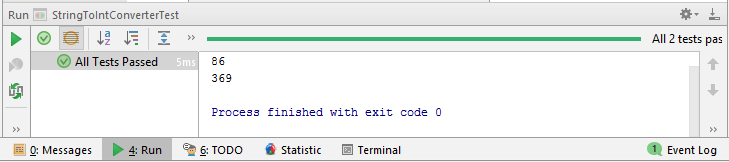
int val= stringToIntConverter.convertWithParseIntWithRadix("1010110", 2);
System.out.println(val);
assertEquals(val, 86);
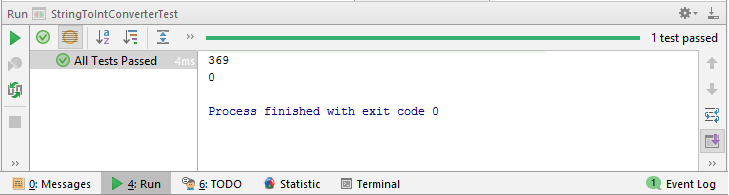
}The output on running the test in InteliJ is this.
Handling Parsing Exception
The parseInt() method throws a NumberFormatException if the String does not contain a parsable int.
Here is a sample code to handle the NumberFormatException gracefully.
public static final int DEFAULT_DEFAULT_PARSED_INT = 0;
public int tryConvertWithParseInt(String str){
try {
int number = Integer.parseInt(str);
return number;
}
catch(NumberFormatException e){
return DEFAULT_DEFAULT_PARSED_INT;
}
}This code returns a default int value whenever a NumberFormatException is thrown by the parseInt() method.
Here is the JUnit test code.
@Test
public void tryConvertWithParseInt() {
int valA = stringToIntConverter.tryConvertWithParseInt(str);
int valB = stringToIntConverter.tryConvertWithParseInt("abc");
System.out.println(valA);
assertEquals(valA, 369);
System.out.println(valB);
assertEquals(valB, 0);
}The Integer.valueOf Method
The Integer class also comes with the static valueOf() method to convert String to int. The valueOf() method interprets the String exactly as if it were given to parseInt(). In fact, the valueOf() method internally uses the parseInt() method.
However, valueOf() returns a new Integer object whereas parseInt() returns a primitive int.
The code to parse String using the valueOf() method is this.
public Integer convertWithValueOf(String str){
try {
Integer num = Integer.valueOf(str);
return num;
}
catch(NumberFormatException e){
return DEFAULT_PARSED_INT;
}
}Here is the JUnit test code.
@Test
public void convertWithValueOf() {
int val= stringToIntConverter.convertWithValueOf(str);
System.out.println(val);
assertEquals(val, 369);
}
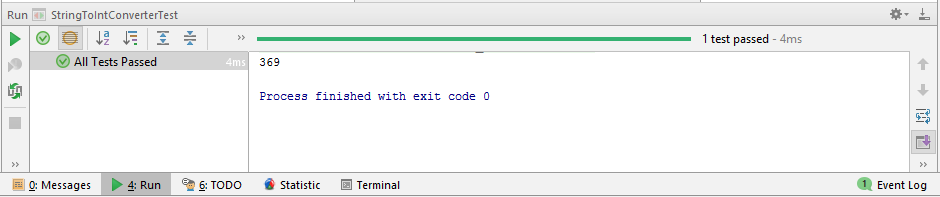
The test output is this.
Note: Similar to parseInt(), the valueOf() method also have an overloaded version that accepts an additional radix value.
Conclusion
Considering Java is a strongly typed language and often interfaces with systems that do not have the type system of Java, converting from a string value to an int value in Java is very common task. As you can see Java provides a number of different ways to convert a string value to an integer value.