How to Configure Log4J2 Using Yaml
8 CommentsLast Updated on October 21, 2024 by jt
Log4J 2 introduces configuration support through JSON and YAML in addition to properties file and XML. If you are new to Log4J2, I suggest going through my introductory post on Log4J 2, Introducing Log4J 2 – Enterprise Class Logging.
For the different Log4J 2 configuration options, you can explore these related posts:
- Log4J 2 Configuration: Using Properties File
- Log4J 2 Configuration: Using XML
- Log4J 2 Configuration: Using JSON
In this post, I will discuss how to configure Log4J 2 with YAML.
Maven Dependencies for YAML Configuration
To use Log4J2, you need to add the required Log4J 2 dependencies in your Maven POM, as described here. For YAML configuration, you additionally need Jackson, a suite of data-processing tools for Java. The YAML support for Log4J 2 uses two Jackson packages: Jackson data format and Jackson data bind whose dependencies must be present in your Maven POM.
The following code snippet shows the dependencies required to use YAML to configure Log4J 2.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-yaml</artifactId>
<version>2.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
. . .
Creating a Logger
Before we start configuring Log4J 2 using YAML, lets create a logger class that uses the Log4J 2 API to log messages.
Log4J2YamlConf.java
package guru.springframework.blog.log4j2yaml;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
public class Log4J2YamlConf {
private static Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger();
public void performSomeTask(){
logger.debug("This is a debug message");
logger.info("This is an info message");
logger.warn("This is a warn message");
logger.error("This is an error message");
logger.fatal("This is a fatal message");
}
}We will use JUnit to test the preceding class.
Log4J2YamlConfTest.java
package guru.springframework.blog.log4j2yaml;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class Log4J2YamlConfTest {
@Test
public void testPerformSomeTask() throws Exception {
Log4J2YamlConf log4J2YamlConf = new Log4J2YamlConf();
log4J2YamlConf.performSomeTask();
}
}Configuring Console and File Appenders
In order to configure Log4J 2 using YAML, you need a YAML configuration file, named either log4j2.yaml or log4j2.ym in the project classpath.
The skeleton of a YAML configuration file is this.
Configuration: Properties: Appenders: Loggers:
The syntax of the log4j2.yaml file above is composed of a Configuration key with a list of properties: Properties, Appenders, and Loggers.
Let’s start by configuring two appenders to write log messages to the console and a file. We will also configure an application-specific logger and the root logger to use the appenders, like this.
Configutation:
name: Default
Properties:
Property:
name: log-path
value: "logs"
Appenders:
Console:
name: Console_Appender
target: SYSTEM_OUT
PatternLayout:
pattern: "[%-5level] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %c{1} - %msg%n"
File:
name: File_Appender
fileName: ${log-path}/logfile.log
PatternLayout:
pattern: "[%-5level] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %c{1} - %msg%n"
Loggers:
Root:
level: debug
AppenderRef:
- ref: Console_Appender
Logger:
- name: guru.springframework.blog.log4j2yaml
level: debug
AppenderRef:
- ref: File_Appender
level: error
In the configuration code above:
- Line 4 – Line 7: We declared a
log-pathproperty accessible to the other parts of the configuration code. - Line 9 – Line 21: We configured the
ConsoleandFileappenders. - Line 23 – 35: We configured an application-specific logger for all the logger classes of the
guru.springframework.blog.log4j2yamlpackage. This logger writes error and higher level log messages to the file appender. We also configured the root logger to log debug and higher level messages to the configured console appender.
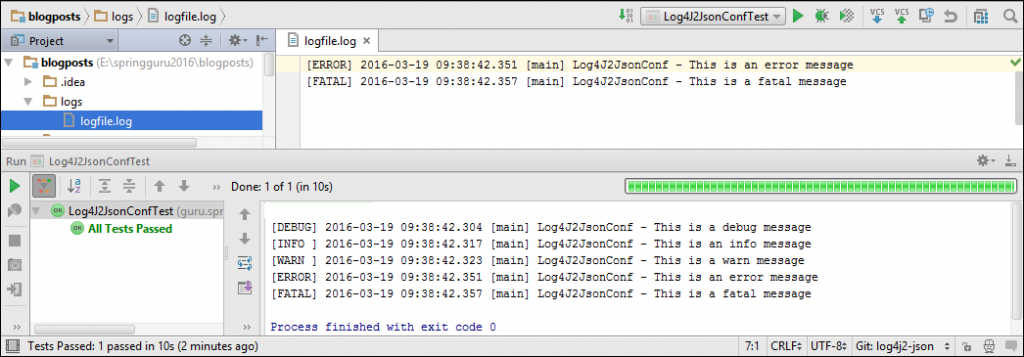
If we run the Log4J2YamlConfTest test class, Log4J 2 will generate log messages and send them both to the console and file, as shown in this figure.
Configuring a Rolling File Appender
In my earlier posts on configuring Log4J 2 using XML and JSON, I discussed about the benefits of the rolling file appender and how to configure one. Additionally, you can refer the Log4J 2 manual to learn more about the rolling file. In YAML, you can configure a rolling file appender, like this.
. . .
RollingFile:
- name: RollingFile_Appender
fileName: ${log-path}/rollingfile.log
filePattern: "logs/archive/rollingfile.log.%d{yyyy-MM-dd-hh-mm}.gz"
PatternLayout:
pattern: "[%-5level] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %c{1} - %msg%n"
Policies:
SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy:
size: 1 KB
DefaultRollOverStrategy:
max: 30
. . .
In the code above:
- Line 3: We used the
namevalue ofRollingFileto define a name of this appender that loggers can use. - Line 4 – Line 5: We used the
filenameandfilePatternvalues to define the name of the file to write to and the pattern of the file name of the archived log file respectively. - Line 8 -Line 10: We used the
Policiesproperty to define a sized-based triggering policy. For testing purpose, we set thesize: 1 KBvalue to roll the log file once its size exceeds 1 KB. - Line 11 – Line 12: We used the
DefaultRolloverStrategyproperty with themax: 30value. This instructs Log4J 2 to keep up to 30 rolling files before deleting them.
To use the rolling file appender, add the appender reference to the logger, like this.
. . .
Loggers:
Root:
level: debug
AppenderRef:
- ref: Console_Appender
Logger:
- name: guru.springframework.blog.log4j2yaml
level: debug
AppenderRef:
- ref: File_Appender
level: error
- ref: RollingFile_Appender
level: debug
. . .
In Line 15 – Line 16 of the configuration code above, we added a reference to the rolling file appender with the debug level.
On running the Log4J2YamlConfTest test class, a rollingfile.log file is generated in the logs folder with debug and higher level log messages. Now if you run the Log4J2YamlConfTest test class couple of more times till the size of the rollingfile.log file exceeds 1 KB, Log4J 2 creates a .gz archive of the generated rolling file in the archive directory.
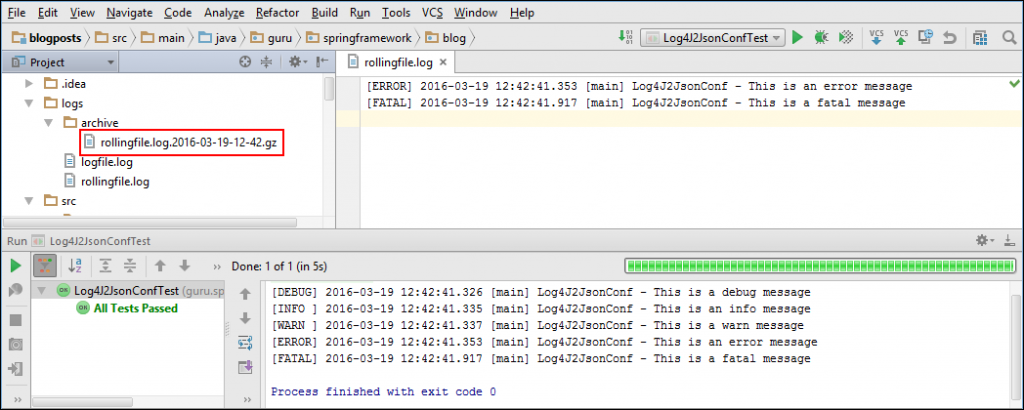
Logging Additivity
So far in our example, we have been using additivity to send messages sent to the file appender also to the console appender. You can override this default behavior by setting the additivity property of a logger to false.
The complete code of the log4j2.yaml file without additivity is this.
log4j2.yaml
Configuration:
name: Default
Properties:
Property:
name: log-path
value: "logs"
Appenders:
Console:
name: Console_Appender
target: SYSTEM_OUT
PatternLayout:
pattern: "[%-5level] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %c{1} - %msg%n"
File:
name: File_Appender
fileName: ${log-path}/logfile.log
PatternLayout:
pattern: "[%-5level] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %c{1} - %msg%n"
RollingFile:
- name: RollingFile_Appender
fileName: ${log-path}/rollingfile.log
filePattern: "logs/archive/rollingfile.log.%d{yyyy-MM-dd-hh-mm}.gz"
PatternLayout:
pattern: "[%-5level] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %c{1} - %msg%n"
Policies:
SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy:
size: 1 KB
DefaultRollOverStrategy:
max: 30
Loggers:
Root:
level: debug
AppenderRef:
- ref: Console_Appender
Logger:
- name: guru.springframework.blog.log4j2yaml
additivity: false
level: debug
AppenderRef:
- ref: Console_Appender
level: info
- ref: File_Appender
level: error
- ref: RollingFile_Appender
level: debugIn Line 47 – Line 48 of the code above, we configured a console appender with the level info for our logger. We also disabled additivity in Line 44 by adding the additivity: false value.
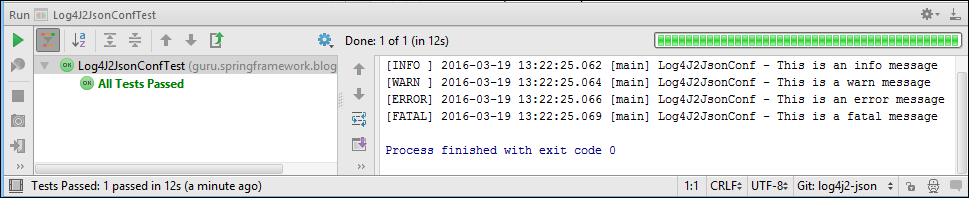
Now, when we run the test class, our logger will use the newly configured console appender instead of the one in the root logger. You can run the test class again to check that info and higher log messages are now getting sent to the console, as shown in this figure. You can see the debug level is no longer sent to the console.
For configuring additivity using XML and JSON, refer my earlier posts here, and also here. I also suggest reviewing the Log4J 2 documentation on the subject, where they have some good examples how this works.
Summary
Out of all the configuration options, YAML is the most compact and readable format. However, unlike properties and XML configurations, you need the additional Jackson JARs in your project to parse the YAML configuration file. If you are familiar with the XML or JSON format, you can use one of the several converters to convert your XML or JSON configurations to YAML, and also the other way around. One of the tools you can try is an online converter available here. However, as a note of caution, converters are not always 100% accurate. As a developer, use it for reference.



























Serkan
can we store this log4j2.yaml in the spring-cloud-config-server ?
jt
I’m not sure if you can or not.
Sumanth Duvvuru
is anyone aware wheather this log4j2.yaml be stored in config-server..??
Sandeep
Can any one tell me how to assign dynamic value to value: field in the below configuration. I am able to set logging.path in application.yml file from command line arguments. Bu thow can i pass on this value to log4j2.yml
Properties:
Property:
name: log-path
value: “logs”
Andrew Louth
Spelling mistake on ‘Configuration’ in the first example yaml.
Mounica
Hi,
Could you help me in resolving the below issue while trying to load log4j2 in YAML format. It appears when trying to run SpringBootApplication.
ERROR StatusLogger Error parsing C:\git\JDF-RecordRetention\LoggingServiceAPI\target\classes\log4j2.yaml
com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.snakeyaml.error.MarkedYAMLException: mapping values are not allowed here
in ‘reader’, line 19, column 14:
fileName: ${basePath}/logfile.log
Caused by: mapping values are not allowed here
in ‘reader’, line 19, column 14:
fileName: ${basePath}/logfile.log
^
java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.json.JsonConfiguration.setup(JsonConfiguration.java:112)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.AbstractConfiguration.initialize(AbstractConfiguration.java:239)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.AbstractConfiguration.start(AbstractConfiguration.java:288)
Patel Jay
YAML is good but using JSON is a very understanding language. for modifying JSON Parser is the best tool.
https://jsonparser.org/
Mostafa Abdelhamid Atwa
What about utilizing a custom appender for testing purposes?